
Galvanized Steel Coil
Width : 1000-4000mm,etc
Length: 2000mm, 2438mm, 3000mm, 3500,6000mm,12000mm,or rolled,etc etc
Standard: ASTM,AISI,JIS,GB, DIN,EN
Certification: ISO, SGS,BV
Galvanization is a manufacturing process involving the application of zinc coating to steel to prevent it from rusting. The zinc coating works to protect the base metal. It does this by acting as a barrier to the various corrosive elements. Therefore, it offers a sacrificial nature that gives a high-quality and long-lasting steel product.
Galvanized sheet metal is one of the most popular types of steel. This is due to its increased strength, extended durability, and formability. The corrosion-resistant property throws its usefulness up a significant notch.
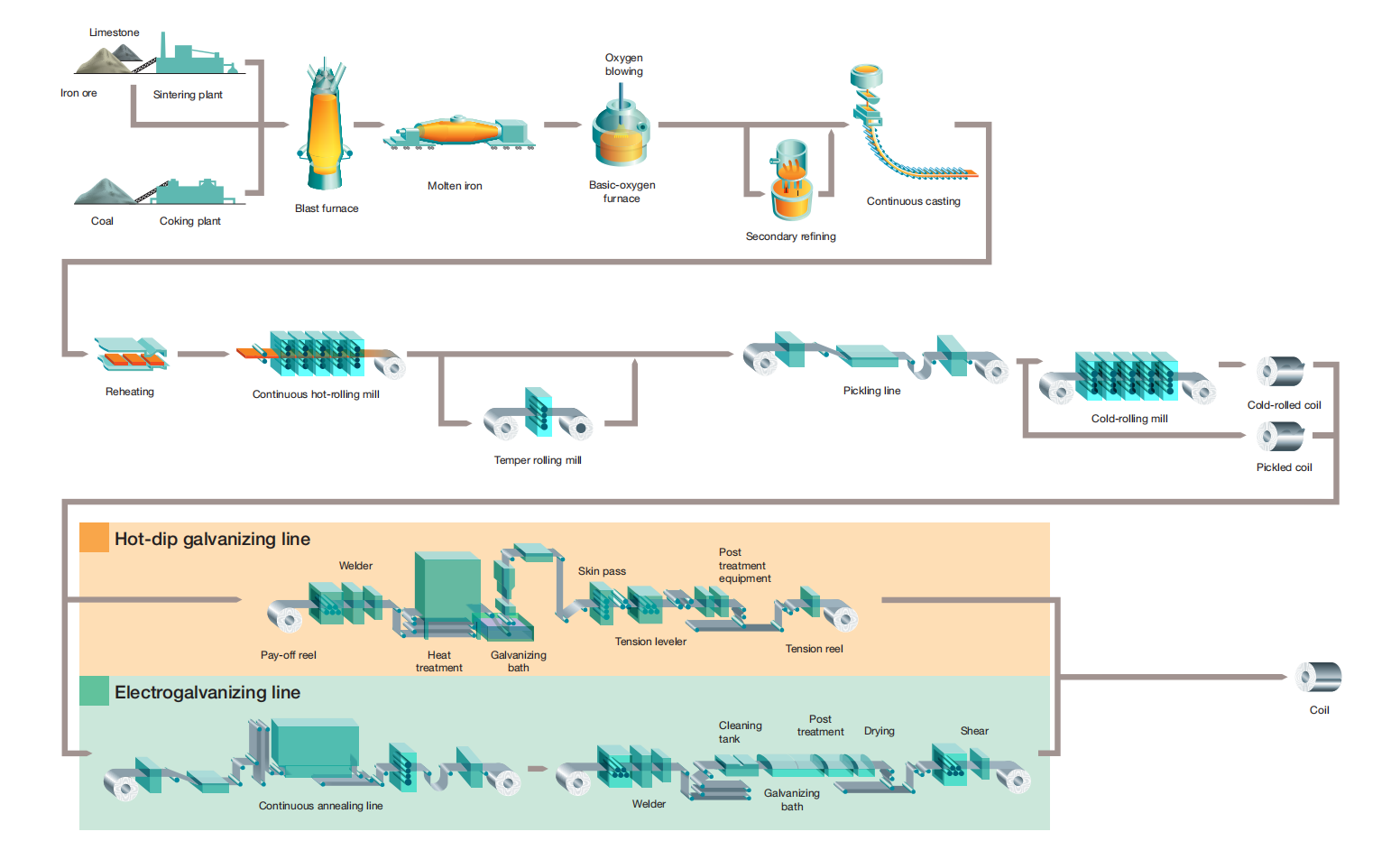
PROCESS TYPES
Types of Galvanizations
There is a wide variety of galvanization types for corrosion protection. Each of these types has its unique performance and characteristics.
Following is a brief description of the various types of galvanizations.
Hot-Dip Galvanization
Hot-dip galvanization is the most widely used method of galvanization. Just as its name suggests, it involves the dipping of the steel in molten zinc.
The pool of molten zinc often maintains a temperature of about 860°F (460 °C).
After proper cleaning of the base metal chemically, it gets fluxed to eliminate residual oxides.
A metallurgical bond begins to form between the zinc and the intended metal.
After pulling the metal from the bath, the pure zinc mixes with oxygen from the atmosphere to form zinc oxide.
Then, the zinc oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form zinc carbonate.
The zinc carbonate makes the final coating on the base metal.
Electro Galvanization
Unlike the hot-dip method, this type does not use a molten zinc bath. Rather,
it uses an electrical current in an electrolyte solution to transfer the zinc ions into the metal.
The positively charged zinc ions are reduced electrically and deposited on the charged material.
It offers the benefit of precise and uniform coating thickness.
Specification And Size
| CNS 1244 2013 | JIS G 3302 2019 | ASTM A653M 2017 | AS1397 2011 | EN 10346 2015 | |||
| Specifications | Hot-rolledBase :SGHC 340 400 440 490 540 | Cold-rolled Base: SGCC SGCD 1~3 SGC 340 400 440 490 570 | Hot-rolled Base: SGH 340 400 440 490 540 | Cold-rolled Base: 1~3 SGC 340 400 440 490 570 | DS DDS CS TYPE A, B, C FS TYPE A, B SS GRADE 33(230) 37(255) 40(275) 50(340)CLASS 1~3 80(550)CLASS 1~3 | G1~G3 G250 300 350 400 450 550 | DX51-52-53D S220GD (250 280 320 350 550) |
| Thickness of Base Steel (mm) | 1.2~4.60 | SGCD1~3: 0.27~2.0mm SGCC/SGC: 0.19~2.0mm | 1.2~4.60 | SGCC, SGC340: 0.18~3.0mm; SGCD1~3: 0.25~2.0mm; SGC400,440: 0.229~3.0mm; SGC490: 1.8~3.0mm; SGC570: 0.229~2.2mm | DS: 0.27~2.0mm; DDS: 0.25~2.0mm; CS/FS: 0.19~4.50mm; SS GRADE 33~80: 0.19~4.50mm; CS TYPE A, B, C, Grade 33, 37: 0.18~3.0mm; FS TYPE A, B: 0.295~2.0mm; Grade 40, 50: 0.229~3.0mm; Grade 55(380): 0.35~3.0mm; Grade 60(410): 0.47~1.6mm; Grade 65(450): 0.229~2.2mm | G1: 0.19~4.50mm; G2&G3: 0.27~2.0mm; G250~550GD: 0.19~4.6mm; G300: 0.229~2.3mm; G350: 0.229~3.0mm; G450: 0.6~3.0mm; G500: 1.1~2.5mm; G550: 0.229~2.2mm | DX51D: 0.19~4.50mm; S220~550GD: 0.19~4.6mm; S250GD: 0.18~2.02mm; DX52D: 0.295~2.0mm; DX53D, 54D: 0.25~2.0mm; S280GD, S350GD: 0.229~3.0mm; S320GD: 0.229~2.3mm; S550GD: 0.229~2.2mm |

Applications
Automotive Industry
The use of galvanized steel on vehicles dates many years back. Using zinc-coated bodies on automobiles has become the norm of car manufacturing. The rust-resistant nature of this material makes it a great marketing tool in the competitive market. Several makers leverage them to offer anti-rust warranties to their customers.
Telecommunication Industry
Maintaining phone lines isn’t an easy job. They require the toughest and most reliable materials for success. Galvanized sheet metal offers its uses on phone wiring and equipment boxes. Therefore, there will be decreased danger of injury and reduced maintenance cost.
Electric Equipment and Appliances
When you look at most electric appliances around you, you may be able to notice the unique features of their casing. Most casings for electrical equipment use galvanized steel material. In fact, it is not surprising that some interior parts of these appliances are made from this steel material.
Building and Construction Industry
The sturdiness and durability that galvanized sheet metal offers make it popular in the construction industry. It has been employed in various commercial and residential projects to the highest level.




.png) info@baowusteel.net
info@baowusteel.net.png) Room 1201-2232,Floor 12,Chenjing Building(Yizhongbao Industrial Park), Hedong District,Tianjin
Room 1201-2232,Floor 12,Chenjing Building(Yizhongbao Industrial Park), Hedong District,Tianjin